What is a Sitemap? A Guide to Creating and Submitting a Sitemap to Google
- Published on

- What is a Sitemap?
- Sitemap as the bridge between your website and search engines
- Types of Sitemaps: HTML Sitemap and XML Sitemap
- HTML Sitemap (For Users)
- XML Sitemap (For Search Engines)
- Specialized Sitemap Types
- Benefits of Sitemap for SEO and User Experience
- Sitemap Benefits for SEO
- Benefits of Sitemap for Users
- The Importance of Sitemap for Different Types of Websites
- How to Check if Your Website Has a Sitemap
- Method 1: Check Sitemap via URL
- Method 2: Use Online Tools
- Common Issues When Checking Sitemaps
- What to Do If Your Website Doesn’t Have a Sitemap?
- How to Create a Sitemap for Your Website
- How to Create an HTML Sitemap
- How to Create an XML Sitemap
- How to Submit a Sitemap to Google Search Console
- How to Split and Optimize Sitemaps for Large Websites
- Benefits of Splitting Sitemaps
- Methods for Splitting Sitemaps
- How to Create a Sitemap Index
- Updating and Checking Sitemaps
- Common Sitemap Issues and How to Fix Them
- Sitemap Contains Invalid URLs
- Outdated Sitemap
- Sitemap Exceeds Size Limits
- URLs Blocked by robots.txt
- Effective Tools for Creating and Managing Sitemaps
- Tools for Sitemap Creation
- Tools for Checking and Optimizing Sitemaps
- Advanced Tools for Sitemap Optimization
- Guidelines for Optimizing Google Bot’s Crawling Speed
- Optimize Page Load Speed
- Leverage Internal Links
- Optimize the robots.txt File
- Example of an Optimized robots.txt File:
- Using Google Search Console
- Minimizing Crawl Errors
- Regularly Update Sitemaps
- Integrating Sitemaps into Your Overall SEO Strategy
- Using Sitemap Data to Optimize Content
- Combining Sitemaps with Internal Link Strategies
- Optimizing Sitemaps for Specific Content Types
- Combining Sitemaps with Link-Building Strategies
- Tracking SEO Performance via Sitemaps
- Conclusion
In the world of modern SEO, building a website is not just about optimizing content; it’s also about ensuring that Google bot can efficiently understand and crawl your website. This is where the role of a Sitemap becomes crucial.
What is a Sitemap?
A Sitemap, also known as a website map, is a file that lists all the URLs on your website, organized in a logical, hierarchical structure. This file acts as a "roadmap" to help search engines like Google or Bing identify:
- Which content should be prioritized for crawling.
- The frequency of updates for each page.
- The connections between the pages on your website.
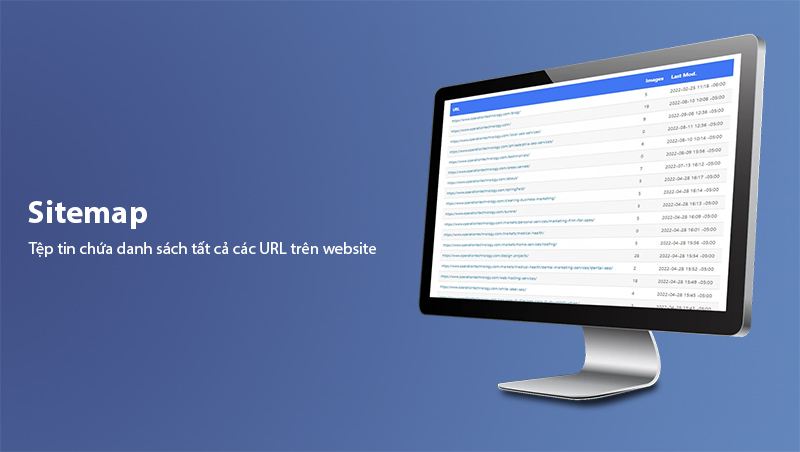
Additionally, a Sitemap is not only useful for search engines but also helps users navigate a website more easily via an HTML Sitemap.
Sitemap as the bridge between your website and search engines
Not all URLs on your website can be automatically discovered by search engines. A Sitemap acts as a "ticket" to ensure that no important content is missed. Consider creating a Sitemap as the first step to helping your website achieve higher rankings on search engines.
Types of Sitemaps: HTML Sitemap and XML Sitemap
To maximize the potential of a Sitemap, it’s important to understand the two main types: HTML Sitemap and XML Sitemap. Each serves a specific purpose in supporting SEO and enhancing user experience.
HTML Sitemap (For Users)
An HTML Sitemap is a web page designed to help users easily locate content on a website. Presented as a list of links in HTML format, this type of Sitemap is often placed in the footer or auxiliary menu to ensure visitors can quickly access it.
Benefits of HTML Sitemap:
- Enhances user experience (UX):
For websites with extensive categories and content, an HTML Sitemap acts as a guide to help users quickly find what they’re looking for. - Improves SEO effectiveness:
The presence of key phrases in an HTML Sitemap can boost your website’s ranking on search engines. Google highly values websites that offer a positive user experience, which in turn improves rankings.
XML Sitemap (For Search Engines)
An XML Sitemap is designed to assist search engine bots like Google or Bing in efficiently crawling your website. This type of Sitemap provides detailed information about:
- Important URLs on your site.
- The frequency of content updates.
- The last modified date of each URL.
- The priority levels between pages.

Benefits of XML Sitemap:
-
Speeds up indexing:
For new websites without many internal links or backlinks, an XML Sitemap informs Google about the existence of new URLs. -
Optimizes crawl budget:
For large websites, search engines crawl a limited number of URLs within a specific timeframe. An XML Sitemap prioritizes critical URLs, ensuring no valuable pages are overlooked. -
Ensures accuracy:
When content is copied or cited, an XML Sitemap helps Google identify the original source, preventing your ranking from being overtaken by duplicate sites.
Additional Tip: How to improve Google indexing speed for new websites
Specialized Sitemap Types
Apart from HTML and XML, there are various specialized Sitemaps used for specific purposes:
-
Sitemap Index:
A collection of smaller Sitemaps, ideal for large websites with thousands of URLs. -
Sitemap-category.xml:
Lists primary categories on a website. -
Sitemap-products.xml:
Contains detailed links to products, commonly used for e-commerce websites. -
Sitemap-video.xml:
Dedicated to videos, helping Google understand multimedia content. -
Sitemap-image.xml:
Lists significant images on a website, especially useful for photography or image-selling services.
Benefits of Sitemap for SEO and User Experience
Sitemap Benefits for SEO
A well-optimized website cannot do without a Sitemap. It not only enhances Google’s ability to crawl your site but also lays the foundation for a long-term SEO strategy. Here are its specific benefits:

-
Speeds up the indexing of new content:
When new content is published, a Sitemap directly informs Google about the URLs to be indexed. This is particularly crucial for new websites or those with limited backlinks. -
Ensures no important content is missed:
For large websites with numerous categories and URLs, internal linking may not always be perfect. A Sitemap ensures all content, especially critical pages, is captured by Google bots. -
Optimizes crawl budget:
Google allocates a limited crawl budget per website. A Sitemap enables you to prioritize the most important URLs, ensuring Google bot works more effectively. -
Enhances visibility on search engines:
A properly optimized XML Sitemap can help your website appear with richer search results, such as Rich Snippets or Featured Snippets.
Read More: What are Rich Snippets and how to implement them effectively
Benefits of Sitemap for Users
Beyond supporting SEO, Sitemaps provide significant value in improving user experience (UX):
-
Easy navigation:
With an HTML Sitemap, users can quickly locate the content they need without navigating through excessive categories. -
Improved time on site:
When users can easily find the information they seek, they tend to spend more time on your website, reducing the bounce rate (Bounce Rate)—a factor Google considers when evaluating rankings.
Additional Tip: What is Bounce Rate? How to Reduce Bounce Rate Effectively
The Importance of Sitemap for Different Types of Websites
Not every website requires a Sitemap, but in the following cases, a Sitemap is an indispensable tool:
-
New websites:
New websites with limited content or backlinks greatly benefit from an XML Sitemap, helping Google quickly discover and index pages. -
E-commerce websites:
For websites with hundreds or even thousands of products, a Sitemap assists Google bots in understanding category structures and accurately displaying products in search results. -
Media-centric websites:
Websites focused on videos, images, or downloadable content can utilize specialized Sitemaps like Sitemap-video.xml or Sitemap-image.xml to help Google process multimedia content more effectively.
How to Check if Your Website Has a Sitemap
Before creating or optimizing your Sitemap, you need to check if your website already has one. This helps identify the current status of the Sitemap and discover issues that need to be resolved.
Method 1: Check Sitemap via URL
Most websites with an XML Sitemap store them at a default URL path. You can check this by adding /sitemap.xml to your domain. For example:
https://www.example.com/sitemap.xml
If your website already has a Sitemap, a list of URLs will appear, often including links to sub-Sitemaps such as:
/sitemap-category.xml/sitemap-products.xml/sitemap-articles.xml
If no file is found, it means you need to create a Sitemap immediately.
Note: For CMS-based websites (like WordPress), some SEO plugins automatically generate a Sitemap without manual intervention.
Method 2: Use Online Tools
In addition to manual checking, you can use online tools to automatically check for Sitemaps. Some popular tools include:
- XML Sitemap Validator: Checks the validity of your Sitemap.
- Screaming Frog SEO Spider: Analyzes the complete URL structure of your website, including the Sitemap.
- Google Search Console: Allows you to track the status and errors related to your Sitemap.
Read More: What is Google Search Console? A Complete Guide to GSC
Common Issues When Checking Sitemaps
-
Sitemap not found:
This is common for new websites or those without proper technical optimization. Ensure that you’ve created and submitted a Sitemap to Google. -
Sitemap with structural errors:
Issues such as invalid URLs, improperly formatted XML tags, or missing required attributes (lastmod, priority, changefreq) may cause Google bots to skip certain URLs. -
Outdated Sitemap:
If new content is added but the Sitemap doesn’t update automatically, search engines may fail to recognize the new content.
What to Do If Your Website Doesn’t Have a Sitemap?
If your website doesn’t have a Sitemap, it’s time to create one. Detailed instructions for creating HTML Sitemaps and XML Sitemaps are provided in the following sections:
How to Create a Sitemap for Your Website
Creating a Sitemap is an essential step in SEO optimization, enabling search engines like Google to efficiently crawl your website. Below are easy methods to create both HTML Sitemaps and XML Sitemaps.
How to Create an HTML Sitemap
An HTML Sitemap helps users easily navigate your website, making it especially useful for websites with many categories and content.
Method 1: Create an HTML Sitemap Using a Plugin (WordPress)
If you’re using WordPress, the Simple Sitemap plugin is an optimal choice:
- Step 1: Go to the WordPress Dashboard, navigate to Plugins > Add New, search for and install the Simple Sitemap plugin.
- Step 2: After installation, create a new page and insert the shortcode
[simple-sitemap]into the content area. - Step 3: Publish the page and check if the HTML Sitemap is displayed correctly.
Method 2: Create an HTML Sitemap Manually
If you want complete control over the appearance of the HTML Sitemap, you can create one manually by using the following HTML code:
<ul>
<li><a href="/category-1">Category 1</a></li>
<li><a href="/category-2">Category 2</a></li>
<ul>
<li><a href="/category-2/sub-category-1">Subcategory 1</a></li>
<li><a href="/category-2/sub-category-2">Subcategory 2</a></li>
</ul>
</ul>
You can use CSS to improve the appearance of your HTML Sitemap according to your preferences.

Tip: Place the HTML Sitemap in the footer or menu to make it easy for users to find.
How to Create an XML Sitemap
An XML Sitemap is specifically designed for search engines, helping Google bot easily crawl and index important pages on your website. Below are some popular methods for creating an XML Sitemap.
Method 1: Create an XML Sitemap Using Yoast SEO Plugin (WordPress)
The Yoast SEO plugin is a widely recognized tool for automatically generating XML Sitemaps in WordPress. Here’s how to use it:
-
Step 1:
Go to your WordPress Dashboard, select Plugins > Add New, search for and install the Yoast SEO plugin. -
Step 2:
Once installed and activated, navigate to SEO > General > Features, and enable the XML Sitemaps feature.
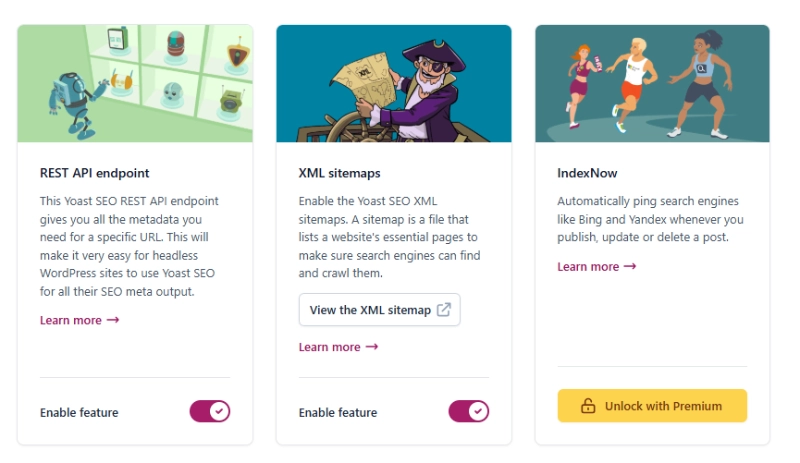
- Step 3:
Verify your XML Sitemap by appending/sitemap_index.xmlto your website’s URL. Example:https://www.example.com/sitemap_index.xml
Method 2: Create an XML Sitemap Using Google XML Sitemaps Plugin
If you don’t use Yoast SEO, the Google XML Sitemaps plugin is a reliable alternative. Follow these steps:
-
Step 1:
In the WordPress Dashboard, go to Plugins > Add New, search for Google XML Sitemaps, and install and activate the plugin. -
Step 2:
Navigate to Settings > XML Sitemap and configure the options:- Choose the types of content to include in the Sitemap: posts, pages, categories, or other types of content.
- Exclude unnecessary URLs: such as error pages, private pages, or irrelevant content.
- Set priority levels: Assign higher priority to important content.
- Set change frequency: Specify how often the content is updated.
-
Step 3:
Check the Sitemap by appending/sitemap.xmlto your website’s URL. Example:https://www.example.com/sitemap.xml
Method 3: Create an XML Sitemap Using Online Tools
If you’re not using WordPress or prefer not to install plugins, online tools like XML-Sitemaps.com provide an easy and effective way to create XML Sitemaps. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
-
Step 1:
Visit XML-Sitemaps.com. -
Step 2:
Enter your website URL into the search bar and click Start to initiate the scanning process. The tool will automatically crawl your entire site and list the available URLs. -
Step 3:
Once the scanning process is complete, download the XML Sitemap file to your computer by clicking Download Your Sitemap. -
Step 4:
Use an FTP client (e.g., FileZilla) or File Manager in cPanel to upload the XML file to the root directory of your website, typically located at:/public_html/ -
Step 5:
Verify the successful upload of your XML Sitemap by visiting the following URL in your browser:https://www.example.com/sitemap.xml
When accessed, the XML Sitemap should display a list of your website’s URLs. If the file doesn’t display or returns an error, check the file path or upload process.
- If no list appears, ensure that the sitemap.xml file is placed in the root directory of your website.
- Confirm that the file permissions on your hosting server allow public access.
How to Submit a Sitemap to Google Search Console
After creating and verifying your Sitemap, the next step is to submit it to Google Search Console so Google can efficiently crawl and index your website content.
Access Google Search Console
- Log in to your Google Search Console account at https://search.google.com/search-console.
- Select the Property corresponding to the website where you want to submit the Sitemap. If your website is not yet added to Google Search Console, you’ll need to verify domain ownership before proceeding.
Submit Your Sitemap
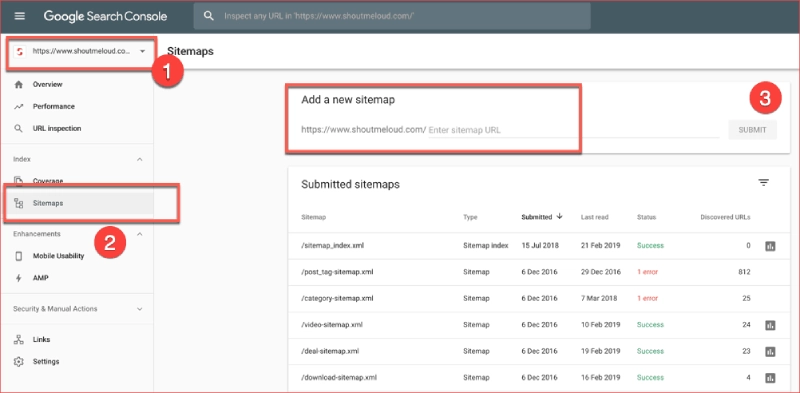
-
Step 1:
From the main dashboard, navigate to Sitemaps in the left-hand menu under the Index section. -
Step 2:
In the Add a new sitemap field, enter the path to your Sitemap (e.g.,sitemap.xml). -
Step 3:
Click the Submit button.
Check the Status of Your Sitemap
After submitting the Sitemap, Google will start crawling the file. You can monitor its status in the Submitted Sitemaps section of Google Search Console:
-
Success:
Indicates that Google has successfully read and accepted the Sitemap. The URLs in the Sitemap will be processed for indexing. -
Error:
If an error occurs, Google may not be able to crawl the Sitemap. Common issues include:- Incorrect sitemap.xml file formatting.
- Invalid or non-existent URLs in the Sitemap.
- File permissions for sitemap.xml not set to public.
How to Fix Errors:
- Use an XML Validator to check the formatting of your sitemap.xml file.
- Ensure the file is stored in the root directory of your website and is publicly accessible.
Monitor Sitemap Performance
Google Search Console not only allows you to submit Sitemaps but also provides detailed insights into their performance. You can monitor:
-
Number of URLs Indexed:
A graph shows how many URLs from your Sitemap Google has crawled and indexed. -
Errors During Crawling:
Common errors include:- URLs blocked by the robots.txt file.
- URLs returning invalid HTTP status codes (e.g., 404 errors, 500 errors).
-
Warnings Related to Content:
Alerts about pages that may need optimization or updates to improve visibility.
Note:
- To achieve effective SEO, regularly check your Sitemap’s performance.
- Update your Sitemap whenever there are significant changes to your website’s structure, such as adding new categories, products, or modifying URLs.
- Consider using additional SEO tools to track overall crawl performance.
Read More: What is a robots.txt file? How to Optimize robots.txt for SEO
How to Split and Optimize Sitemaps for Large Websites
If your website has thousands of URLs, splitting your Sitemap is an essential strategy to ensure search engines can efficiently crawl your content. Here’s a guide to splitting and optimizing Sitemaps for large websites.

Benefits of Splitting Sitemaps
-
Faster Crawling:
Google bots have a limit on how much of a large Sitemap they can process. Splitting Sitemaps helps speed up the crawling process. -
Easier Management:
By dividing the Sitemap based on categories or content types, you can manage and update them separately without affecting the entire website. -
Optimized for Specific Content Types:
Separate Sitemaps for posts, images, and videos ensure that Google processes each type of data more effectively.
Methods for Splitting Sitemaps
-
Split by Content Type:
sitemap-posts.xml: Lists blog posts.sitemap-pages.xml: Lists static pages (e.g., About, Contact).sitemap-products.xml: Lists products (for e-commerce websites).sitemap-images.xml: Lists important image URLs.sitemap-videos.xml: Lists uploaded videos.
-
Split by Category:
- Create separate Sitemaps for each product or post category, such as:
sitemap-electronics.xml(electronics).sitemap-fashion.xml(fashion).
- Create separate Sitemaps for each product or post category, such as:
-
Split by URL Count:
- If the total number of URLs exceeds Google’s limit of 50,000 lines per Sitemap, divide the Sitemap into smaller files, each containing up to 50,000 URLs.
How to Create a Sitemap Index
After splitting your Sitemap into smaller files, you need a Sitemap Index file to link and manage all the sub-Sitemaps. This file allows Google bots to easily locate and crawl all your Sitemaps.
- Example of a Sitemap Index file:
<sitemapindex xmlns="http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9">
<sitemap>
<loc>https://www.example.com/sitemap-posts.xml</loc>
<lastmod>2024-12-01</lastmod>
</sitemap>
<sitemap>
<loc>https://www.example.com/sitemap-products.xml</loc>
<lastmod>2024-12-01</lastmod>
</sitemap>
<sitemap>
<loc>https://www.example.com/sitemap-images.xml</loc>
<lastmod>2024-12-01</lastmod>
</sitemap>
</sitemapindex>
Updating and Checking Sitemaps
Keeping your Sitemap updated and accurate is essential for search engines to quickly index new content. Here's how to manage this effectively:
Automating Sitemap Updates
-
Use plugins or tools:
If you’re using WordPress, plugins like Yoast SEO or Google XML Sitemaps will automatically update your Sitemap whenever you add, edit, or delete content.- Yoast SEO: Automatically adjusts the Sitemap Index to include new URLs for posts, pages, or categories.
- Google XML Sitemaps: Refreshes the Sitemap whenever there are content updates.
-
Benefits of automation:
- Reduces errors from manual management.
- Ensures that new URLs are updated promptly.
Regular Checks
-
Google Search Console:
This is the primary tool for monitoring the status of each Sitemap. Steps to check:- Navigate to the Sitemaps section in Google Search Console.
- Check the status of each submitted Sitemap (e.g., Success, Error).
- Monitor the number of URLs indexed from the Sitemaps.
-
Detect and fix errors:
If Google reports errors when crawling your Sitemap, investigate the following:- URL paths in the Sitemap: Ensure all URLs are correct and functional.
- File accessibility: Verify that the sitemap.xml file is set to public.
- File validity: Use tools like XML Validator to check the file format and resolve issues if needed.
Tip: Schedule monthly checks for your Sitemap or review it after significant website changes to ensure accurate data collection.
Common Sitemap Issues and How to Fix Them
While Sitemaps are a powerful SEO tool, improper usage can lead to errors that affect data crawling and indexing by Google. Below are common issues and solutions:
Sitemap Contains Invalid URLs
Issue Description:
- The Sitemap includes URLs that lead to error pages (404), deleted pages, or URLs with incorrect formats.
- This causes difficulties for Google bot in crawling your site.
Solution:
- Use tools like Screaming Frog SEO Spider to scan all URLs in your Sitemap.
- Remove invalid URLs or update the file with accurate URLs.
Outdated Sitemap
Issue Description:
- When new content is added to the website, but the Sitemap isn’t updated automatically, Google cannot identify new URLs for indexing.
Solution:
- Use plugins like Yoast SEO or Google XML Sitemaps to automate updates.
- If you manage the Sitemap manually, regularly check and add new URLs to the file.
Sitemap Exceeds Size Limits
Issue Description:
- Google limits a single Sitemap to 50,000 URLs or 50MB (compressed).
Solution:
- Split the Sitemap into smaller files (e.g.,
sitemap-posts.xml,sitemap-categories.xml, etc.). - Create a Sitemap Index to link all sub-Sitemaps.
URLs Blocked by robots.txt
Issue Description:
- Some URLs in the Sitemap are blocked by the robots.txt file, preventing Google bot from crawling them.
Solution:
- Check the robots.txt file at
https://www.example.com/robots.txt. - Ensure important URLs are not blocked by
Disallow. For example:
Disallow: /wp-admin/
Allow: /wp-content/uploads/
Not Submitting Sitemap to Google
Issue Description:
The Sitemap has been created but has not been submitted to Google Search Console, preventing Google from discovering the file for crawling.
Solution:
- Log in to Google Search Console at https://search.google.com/search-console.
- Go to the Sitemaps section from the left-hand menu.
- Enter the path of your Sitemap (e.g.,
sitemap.xml) in the Add a new sitemap field and click Submit. - Check the status of the Sitemap to ensure it has been successfully received by Google.
Duplicate Content in Sitemap
Issue Description:
The Sitemap contains multiple URLs pointing to the same content, wasting crawl budget and causing Google bot confusion in determining the canonical URL.
Solution:
- Use canonical URLs:
Add arel="canonical"tag in the HTML of the page to specify the preferred URL.
Example:<link rel="canonical" href="https://www.example.com/canonical-page" /> - Remove Duplicate URLs:
- Use tools like Screaming Frog or Sitebulb to identify and eliminate duplicate URLs from the Sitemap file.
Non-Compliant Sitemap Format
Issue Description:
The Sitemap file does not adhere to XML standards, causing Google to be unable to read or process the file. Common errors include:
- Missing
<urlset>tags in the XML file. - Improperly encoded special characters.
- URLs exceeding length limits or containing invalid characters.
Solution:
-
Use an XML Validator:
- This tool checks the validity of the Sitemap file according to the Sitemap Protocol standards. Example: https://www.xml-sitemaps.com/validate-xml-sitemap.html.
-
Edit the file to comply with the Sitemap Protocol:
Ensure that the Sitemap file structure follows the required format. Here is an example of a valid XML Sitemap:<urlset xmlns="http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9"> <url> <loc>https://www.example.com/</loc> <lastmod>2024-12-01</lastmod> <changefreq>daily</changefreq> <priority>1.0</priority> </url> </urlset>
Effective Tools for Creating and Managing Sitemaps
To create and manage Sitemaps effectively, you need specialized tools. Below is a list of the most popular tools that make it easy to create, check, and optimize Sitemaps for your website.
Tools for Sitemap Creation
Yoast SEO (WordPress)
- Features:
- Automatically generates XML Sitemaps for posts, pages, categories, and tags.
- Provides options to enable/disable and customize the content appearing in the Sitemap.
- Intended Users:
WordPress users, especially beginners in SEO.
Google XML Sitemaps (WordPress)
- Features:
- Creates detailed XML Sitemaps with advanced customization options.
- Automatically updates the Sitemap when new content is added.
- Intended Users:
Suitable for WordPress websites not using Yoast SEO.
XML-Sitemaps.com
- Features:
- Free online tool for quickly generating Sitemaps.
- Free version limits to 500 URLs, suitable for small websites.
- Intended Users:
Websites not using CMS or requiring manual Sitemap creation.
Tools for Checking and Optimizing Sitemaps
Google Search Console
- Features:
- Submit Sitemaps to Google and track crawl status.
- Detect issues related to the Sitemap (broken URLs, invalid URLs, or blocked URLs).
- Intended Users:
All websites seeking to optimize Google’s crawl process.
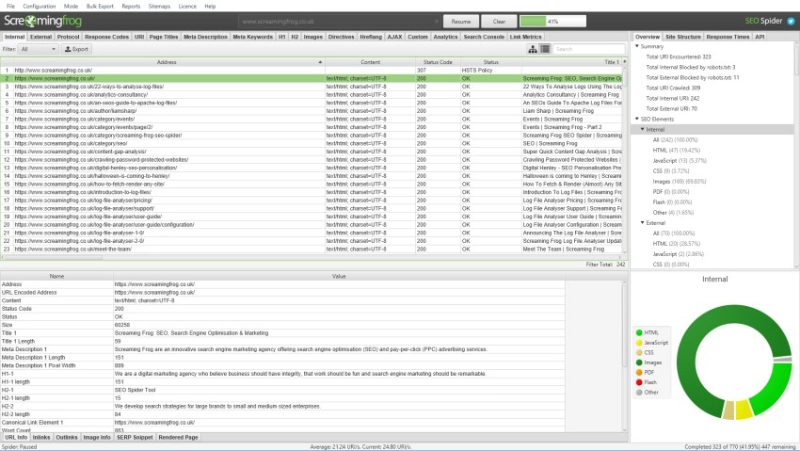
Screaming Frog SEO Spider
- Features:
- Analyzes Sitemaps and checks for issues such as broken URLs, duplicates, or orphaned pages.
- Supports direct Sitemap file export.
- Intended Users:
Large websites requiring in-depth technical checks.
Ahrefs or SEMrush
- Features:
- Checks whether URLs in the Sitemap are indexed.
- Assesses technical SEO factors related to Sitemaps.
- Intended Users:
SEO professionals seeking comprehensive analysis.
Advanced Tools for Sitemap Optimization
Sitebulb
- Features:
- Combines technical SEO audits with detailed website structure analysis.
- Evaluates the efficiency of Sitemaps in aiding indexing.
- Intended Users:
Large or complex websites requiring deep optimization.
Botify
- Features:
- Optimizes crawl budget by analyzing important URLs in the Sitemap.
- Suggests Sitemap adjustments based on performance data.
- Intended Users:
Large enterprises with advanced technical SEO needs.
Guidelines for Optimizing Google Bot’s Crawling Speed
After deploying and submitting a Sitemap, optimizing Google Bot’s crawling speed is essential to ensure new or updated content is indexed promptly. Below are effective optimization methods.
Optimize Page Load Speed
Google prioritizes websites with fast load times. To improve this:
- Image Optimization:
Use compressed formats like WebP and adjust image sizes appropriately. - Implement Caching Systems:
Install plugins like WP Super Cache or W3 Total Cache for WordPress. - Upgrade Hosting:
Ensure your hosting is fast and reliable, especially for high-traffic websites. - Check Page Speed:
Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights to identify bottlenecks and improve them.
Leverage Internal Links
Internal links help Google Bot navigate between pages on your website more easily, speeding up the crawl process.
- Create Logical Link Structures:
Ensure important pages have sufficient internal links from the homepage or main categories. - Use Descriptive Anchor Texts:
Clear anchor texts help Google better understand the target page’s content.
Tip: Increase links to newly published pages to prioritize their crawling by Google Bot.
Optimize the robots.txt File
The robots.txt file allows you to control which pages Google Bot can crawl, optimizing your crawl budget.
- Allow Crawling of Important Pages:
Ensure critical pages like posts or product pages are not blocked byDisallow. - Block Unnecessary Pages:
Prevent crawling of admin pages (/wp-admin/) or internal search result pages (/search/).
Example of an Optimized robots.txt File:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /wp-admin/
Disallow: /search/
Allow: /
Sitemap: https://www.example.com/sitemap.xml
Using Google Search Console
Monitor Crawl Status:
- Access Google Search Console and open the Crawl Stats section.
- Here, you can view how many pages Googlebot has crawled from your website over a specific period.
- Analyze frequently crawled URLs to optimize your content strategy.
Submit Indexing Requests:
- When publishing new content or updating existing pages, use the Inspect URL feature in Google Search Console to request immediate indexing by Google.
- This is especially useful for important URLs that need quick visibility in search results.
Minimizing Crawl Errors
Errors such as 404 Not Found or 500 Internal Server Error can severely impact Googlebot’s crawl efficiency, wasting your crawl budget. To minimize these errors:
-
Check and Fix URL Errors:
- Use tools like Screaming Frog SEO Spider or Ahrefs to scan your entire website, identify broken URLs, and fix them.
- Remove or repair invalid URLs.
-
Use 301 Redirects:
- Redirect broken URLs to pages with related content or to the homepage.
- Ensure both users and Googlebot encounter no errors when navigating your site.
Regularly Update Sitemaps
-
Automated Updates:
- Use plugins like Yoast SEO or Google XML Sitemaps to automatically refresh the Sitemap whenever new content is added or existing content is changed.
- This ensures that Googlebot always crawls the most up-to-date URLs.
-
Periodic Sitemap Checks:
- Regularly review your Sitemap to ensure:
- It does not include broken or duplicate URLs.
- It excludes deleted or outdated content.
- It accurately reflects the current structure of your website.
- Use Google Search Console to monitor the status of your Sitemap and resolve any errors.
- Regularly review your Sitemap to ensure:
Tip: Schedule monthly checks of your Sitemap and crawl status to maintain long-term SEO efficiency.
Integrating Sitemaps into Your Overall SEO Strategy
Using a Sitemap isn’t just about technical aspects; it should also be integrated into your overall SEO strategy. This helps maximize your website’s visibility on search engines and improve user experience.
Using Sitemap Data to Optimize Content
-
Analyze Indexed URLs:
- Use Google Search Console to see which URLs in the Sitemap are indexed the most.
- Evaluate the content of less frequently indexed URLs to improve quality or optimize keywords.
-
Optimize Content Based on Keywords:
- Focus on relevant keywords for important URLs listed in the Sitemap.
- Update titles (Title Tags) and descriptions (Meta Descriptions) to boost click-through rates (CTR).
Combining Sitemaps with Internal Link Strategies
-
Increase Internal Links to Sitemap URLs:
- This helps Googlebot access priority pages more easily.
- Articles or products in the Sitemap should be linked from the homepage or other popular pages.
-
Use User-Friendly URL Structures:
- URLs in the Sitemap should be concise, clear, and include primary keywords.
Optimizing Sitemaps for Specific Content Types
-
Sitemap-video.xml:
- If your site includes videos, create a dedicated video Sitemap.
- Include detailed information such as duration, descriptions, and thumbnails to enhance visibility on Google Videos.
-
Sitemap-image.xml:
- For websites with numerous images (e.g., e-commerce or photography sites), ensure all significant images are included in the Sitemap.
-
Sitemap-news.xml:
- News websites can use a dedicated news Sitemap to ensure Google quickly indexes time-sensitive content.
Combining Sitemaps with Link-Building Strategies
-
Include Sitemap URLs in Backlink Campaigns:
- Build backlinks to key URLs listed in the Sitemap.
- URLs with more backlinks are more likely to be indexed and rank higher.
-
Use Sitemaps for Collaboration Opportunities:
- Partners can reference the Sitemap to identify relevant content for collaborations and link exchanges.
Tracking SEO Performance via Sitemaps
-
Google Search Console:
- Monitor the performance of URLs in the Sitemap, including indexing rates, clicks, and impressions.
-
Analyze and Improve:
- Review URLs that are not indexed or perform poorly and optimize them.
- Remove unnecessary URLs to improve crawl efficiency.
Conclusion
A Sitemap is an indispensable tool in any SEO strategy, especially for large or complex websites. From helping search engines understand the structure of your site and speeding up indexing, to enhancing user experience and improving search rankings, Sitemaps play a crucial role in long-term SEO success.
To maximize the effectiveness of your Sitemap, you should:
-
Create and Manage Sitemaps Properly:
Use automated tools like Yoast SEO, Google XML Sitemaps, or online generators to ensure URLs are always accurately updated. -
Submit Sitemaps to Google Search Console:
Track and fix errors related to the Sitemap to optimize Googlebot’s crawling efficiency. -
Integrate Sitemaps into Your SEO Strategy:
Combine Sitemaps with content optimization, internal linking, and structured data (Schema) to enhance search engine visibility. -
Regularly Review and Improve:
Identify and fix errors, remove unnecessary URLs, and continually optimize the Sitemap to align with the latest SEO trends.
By investing in and maintaining an optimized Sitemap, you not only improve search engine crawling and indexing but also lay a solid foundation for sustainable SEO strategies, enabling your website to grow its organic traffic and enhance its market presence.
Latest Posts

Lesson 26. How to Use break, continue, and return in Java | Learn Java Basics
A guide on how to use break, continue, and return statements in Java to control loops and program execution flow effectively.

Lesson 25. The do-while Loop in Java | Learn Basic Java
A detailed guide on the do-while loop in Java, including syntax, usage, examples, and comparison with the while loop.

Lesson 24. How to Convert Decimal to Binary in Java | Learn Basic Java
A guide on how to convert numbers from the decimal system to the binary system in Java using different methods, with illustrative examples.

Lesson 23. How to Use the While Loop in Java | Learn Java Basics
Learn how to use the while loop in Java with syntax, real-world examples, and practical applications in Java programming.
Related Posts

What is Domain Authority? 13-Step Guide to Improve DA Score for Your Website in 2025
Discover what Domain Authority is and its importance in SEO. A detailed guide on the 13-step process to effectively increase DA, from content research and technical optimization to building quality backlinks for a sustainable SEO strategy.

What is Page Authority? The Importance of Page Authority for SEO in 2025
Learn what Page Authority (PA) is and its role in SEO optimization to help improve your website's ranking on search engines in 2025.

What is Google Index? A Guide to 13 Ways to Speed Up Website Indexing in 2025
Discover what Google Index is and learn detailed guidelines on 13 effective ways to get your website indexed quickly and boost your SEO rankings on Google in 2025.
![What is Onpage SEO? 23+ Basic & Advanced Onpage Optimization Checklist [2025]](/blog-posts/seo-onpage/seo-onpage-thumb.jpg)
What is Onpage SEO? 23+ Basic & Advanced Onpage Optimization Checklist [2025]
Learn the concept of Onpage SEO and the 23+ basic to advanced Onpage optimization checklist to improve website quality and boost search rankings effectively.

