What is Google Analytics? Detailed Guide to Setting Up and Using Google Analytics 2025
- Published on

- What is Google Analytics?
- Purpose and Role of Google Analytics
- Benefits of Google Analytics
- Comprehensive User Data Analysis
- Provides Exclusive Insights
- Integration with Other Platforms
- Boosting Marketing Campaign Efficiency
- Demographic and User Behavior Analysis
- Key Features of Google Analytics
- Intelligent Data Analysis
- Comprehensive Reporting
- Data Customization
- Integration with Other Tools
- How to Set Up Google Analytics
- Register for a Google Analytics Account
- Obtaining the Tracking Code
- Setting Up Google Analytics 4 (GA4)
- Comparison Between Universal Analytics and Google Analytics 4
- Key Metrics to Monitor in Google Analytics
- Users
- Sessions
- Pageviews
- Bounce Rate
- Average Session Duration
- Conversion Rate
- Practical Applications of Google Analytics
- Real-Time Analytics
- Demographic Analysis
- Measuring Marketing Campaign Effectiveness
- Improving User Experience
- Remarketing and Customer Retargeting
- How Google Analytics Works
- Data Collection
- Configuration
- Processing
- Reporting
- Benefits of Understanding the Operational Process
- Guide to Sharing and Managing Google Analytics Data
- How to Share Google Analytics Data
- Efficiently Managing Google Analytics Data
- Integrating Google Analytics with Other Tools
- Common Mistakes When Using Google Analytics
- Incorrectly Implemented Tracking Code
- Not Setting Up Goals
- Ignoring Critical Reports
- Misusing Filters
- Not Integrating with Other Tools
- Conclusion
In the digital era, as competition on the Internet becomes increasingly fierce, understanding user behavior and website performance is the key to business success. However, not everyone knows how to use data to make informed decisions. This is where Google Analytics – Google’s powerful and free website analytics tool – becomes an indispensable assistant for website administrators.
Google Analytics not only helps you track traffic, but also provides detailed information about traffic sources, user behavior, and factors influencing conversion rates. More importantly, this tool allows you to synchronize data with advertising platforms like Google Ads, YouTube, and Facebook, enabling you to optimize your Marketing campaigns effectively. Whether you're managing a personal blog, an online store, or a large corporate website, Google Analytics offers exceptional value in data analysis and improving business efficiency.
In this article, we will explore what Google Analytics is, how to set up and use this tool, and the benefits it offers. If you're looking for a comprehensive solution to analyze and optimize your website, don’t miss any part of this article!
What is Google Analytics?
Google Analytics is a website data analytics tool developed by Google that allows administrators to track, measure, analyze, and report all information related to website activity. From metrics like traffic volume, traffic sources, to user behavior, Google Analytics helps you gain deeper insights into how users interact with your website, enabling you to craft appropriate optimization strategies.
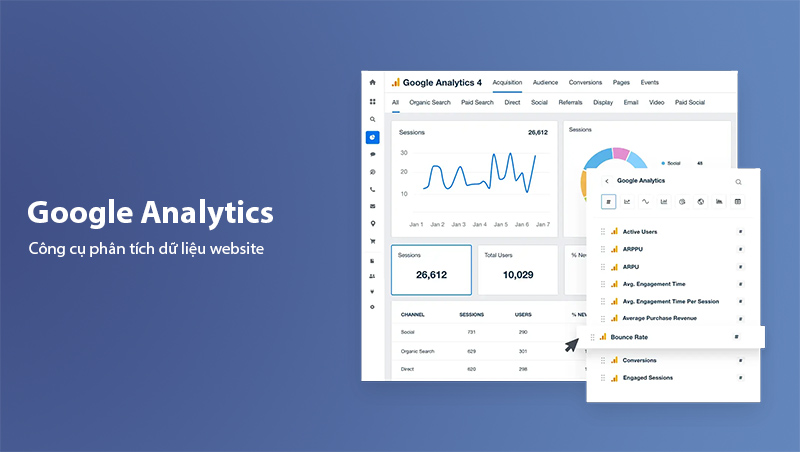
Unlike other analytics tools, Google Analytics provides accurate data collected directly from real user behavior. This tool supports integration with various platforms like Google Ads, YouTube, and Facebook, enabling administrators to synchronize data and build more effective Marketing campaigns.
Purpose and Role of Google Analytics
This tool is not just a reporting system but also a comprehensive analytics platform that helps:
- Evaluate website performance: Monitor traffic, bounce rates, average time on site, and content performance to identify areas for improvement.
- Understand your audience: Analyze demographic data such as age, gender, interests, and geographic location to craft effective outreach strategies.
- Optimize user experience: Use behavioral reports to improve site structure, loading speed, and content to retain users longer.
- Make data-driven decisions: Instead of relying on intuition, Google Analytics provides factual metrics to optimize your SEO and advertising strategies.
If you’re looking to optimize your website to increase conversion rates, check out How to Improve Website Conversion Rates Effectively.
Benefits of Google Analytics
Google Analytics is not just a measurement tool but also a powerful assistant that helps website administrators optimize business performance. Below are the outstanding benefits of Google Analytics:
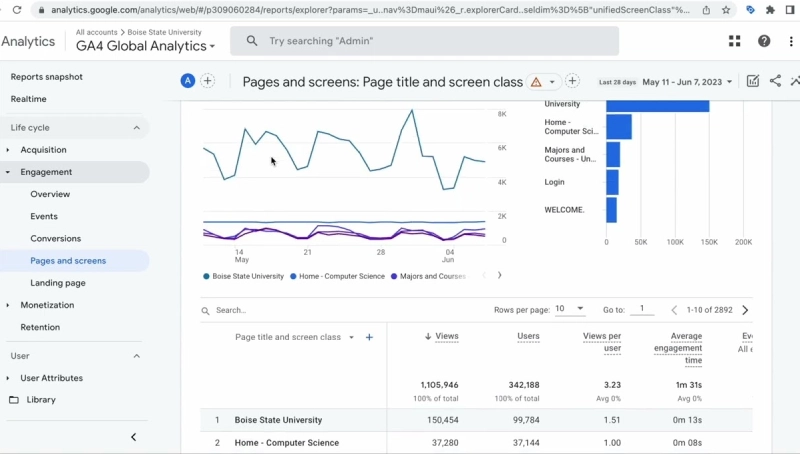
Comprehensive User Data Analysis
Google Analytics provides a full picture of how users interact with your website:
- Traffic: Track the number of visitors to your website from sources like Organic Search, Social Media, Referral, or Direct.
- User behavior: Identify the pages users are most interested in, the actions they take, and the time they spend on the site.
- Bounce Rate (Bounce Rate): Measure the percentage of users who leave the page immediately after visiting without taking any action. A high bounce rate often indicates that the content or interface needs optimization.
Provides Exclusive Insights
Google Analytics helps you discover potential opportunities that your website possesses:
- Analyze the ability to convert users into potential customers.
- Predict customer value based on access behavior, traffic sources, and interaction time.
- Gain better insights into the factors leading to high conversion rates and optimize outreach strategies.
For example, you can identify which product attracts the most views or which traffic source brings in high-value customers.
Integration with Other Platforms
One of the strengths of Google Analytics is its ability to seamlessly integrate data with other advertising and analytics platforms:
- Synchronize with Google Ads, Facebook Ads, and YouTube Ads to track detailed advertising performance.
- Connect with CRM systems or business management tools to create a complete data picture linking website activity and actual revenue.
Boosting Marketing Campaign Efficiency
Google Analytics provides tools for remarketing, allowing you to re-engage customers who have visited your website. This helps:
- Increase conversions: Target the right audience based on their previous behaviors.
- Save advertising costs: Allocate budgets to the most effective advertising channels.
Demographic and User Behavior Analysis
With Google Analytics, you can easily access detailed insights about your website visitors:
- Demographics: Age, gender, and geographic location.
- Interests: Categorize users by different interest groups to tailor content accordingly.
- Traffic sources: Identify which channels bring the highest quality users (Google Search, Social Media, Email Marketing, etc.).
As a result, you can create content strategies, advertising campaigns, and website designs that cater to the needs of specific customer groups.
Key Features of Google Analytics
Google Analytics goes beyond providing basic data, offering standout features that enable administrators to analyze more deeply and optimize websites effectively. Below are the key features you should leverage:
Intelligent Data Analysis
Google Analytics integrates modern technologies like AI and Machine Learning to help you uncover valuable insights from raw data. Some notable features include:
- Smart Goals: Automatically identify objectives based on user behavior and conversion rates.
- Smart Lists: Create potential user lists to optimize remarketing campaigns.
- Session Quality: Evaluate session quality to predict conversion likelihood.
Note: These intelligent features are especially useful for e-commerce businesses or complex marketing campaigns.
Comprehensive Reporting
Google Analytics offers a variety of detailed reports to help you understand every aspect of your website's performance:
- User Reports:
- Track demographics, interests, and traffic sources for different audience groups.
- Behavior Reports:
- Analyze user behavior on your website, from traffic flow to time spent on pages.
- Conversion Reports:
- Assess the effectiveness of each marketing channel and customer journey from visit to transaction.
- Real-Time Reports:
- Instantly monitor the number of users on your website, what content they are viewing, and where they are coming from.
Data Customization
One of the strengths of Google Analytics is its ability to customize data to meet specific needs:
- API Integration: Connect with other tools like Google Data Studio, Salesforce, or third-party software.
- Custom Metrics and Reports: Define key metrics for your business and design dashboards tailored to your needs.
- Variable Configuration: Measure industry-specific metrics, such as revenue per product or conversion rates by region.
Integration with Other Tools
Google Analytics easily integrates with popular tools to create a comprehensive data ecosystem:
- Google Ads: Measure the performance of each ad and optimize costs.
- Google Tag Manager: Manage tracking codes and events without editing the source code directly.
- Google Search Console: Monitor keyword rankings and improve SEO performance.
- Data Studio: Transform raw data into visually appealing, easy-to-understand reports.
How to Set Up Google Analytics
Setting up Google Analytics correctly is the first step to effectively tracking and analyzing website data. Below is a step-by-step guide to help you set up the tool effortlessly:
Register for a Google Analytics Account
- Access Google Analytics:
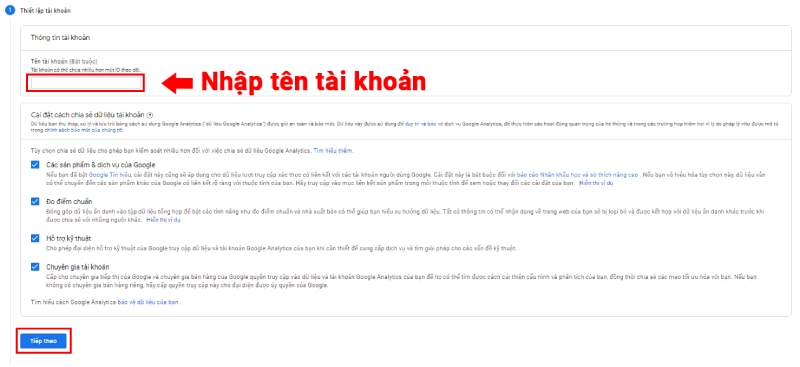
Start by visiting Google Analytics and logging in with your Google account. - Create a new account:
- Click on "Start Measuring" and enter the account name.
- Configure data-sharing settings according to your needs.
-
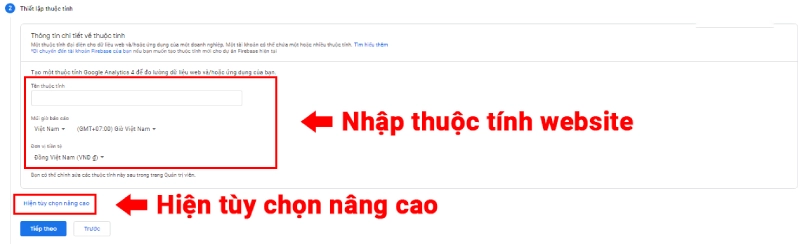
Set up a Property:
- Enter the Property Name, select the reporting time zone, and choose the currency.
- With Google Analytics 4 (GA4), you can set up a single property to track both websites and apps.
- Complete the Setup:
Once the information is filled out, click "Continue", review, and agree to the terms of service to finalize account creation.
Note: If you still need to use the Universal Analytics version, you can enable "Advanced Settings" during the property setup process.
Obtaining the Tracking Code
The Tracking Code is a JavaScript snippet used by Google Analytics to collect data from your website. Here’s how to retrieve and integrate it:
-
Retrieve the Tracking Code:
- Go to the "Admin" section in Google Analytics.
- Select "Data Streams" and click on your website’s name.
- Copy the Measurement ID or the full tracking code provided.
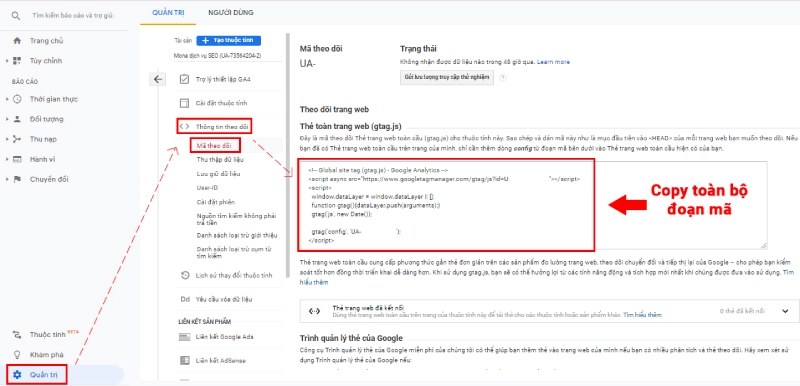
- How to Integrate the Tracking Code:
- For Standard Websites: Insert the tracking code into the
<head>tag on all pages of your website. - For WordPress Websites: Use plugins like Insert Headers and Footers or Google Site Kit to easily integrate the tracking code.
- For Standard Websites: Insert the tracking code into the
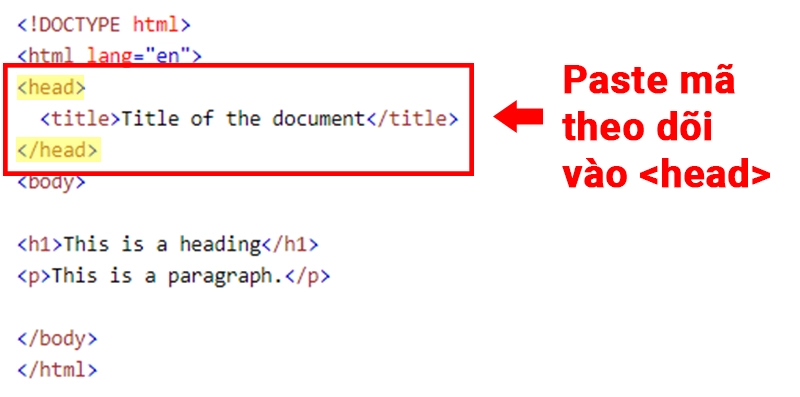
Setting Up Google Analytics 4 (GA4)
Google Analytics 4 (GA4) is the latest version, focusing on comprehensive data tracking and cross-platform user analysis. Follow these steps to set it up:
-
Activate GA4:
- In the Google Analytics interface, go to "Admin" > "GA4 Setup Assistant" > click “Get Started” to create a new GA4 property.
-
Integrate GA4 Code into Your Website:
- If you’re using Google Tag Manager, create a new tag with the configuration Google Analytics: GA4 Configuration and add the Measurement ID from the previous step.
- Activate the tag on all pages and publish the changes.
-
Verify Data Collection:
- After integration, check the "Real-Time Reports" in GA4 to ensure data is being collected correctly.
Comparison Between Universal Analytics and Google Analytics 4
Google recommends transitioning to GA4, but Universal Analytics remains widely used by many businesses. Here’s a quick comparison between the two versions:
| Feature | Google Analytics 4 (GA4) | Universal Analytics (UA) |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement Model | Event-based | Page + Event-based |
| Reporting | Flexible and more intuitive | Traditional interface |
| Conversion Tracking | Mark events as conversions | Configured in admin |
| Data Customization | Supports 50 Custom Dimensions | Supports 20 Custom Dimensions |
| BigQuery Integration | Free | Only available in Analytics 360 |
Installing Google Analytics, whether Universal Analytics or GA4, is a crucial step to start collecting data and optimizing your website. Ensure you follow the steps outlined above to fully leverage the benefits this tool offers.
Key Metrics to Monitor in Google Analytics
When using Google Analytics, understanding and analyzing key metrics will help you evaluate your website’s performance and optimize your business strategy. Below are the most important metrics to focus on:
Users
The Users metric represents the number of unique visitors to your website over a specific time period. Each user is identified by a unique Client ID, allowing Google Analytics to track their behavior on your site.
- Why is this metric important?
Knowing the number of users helps you assess your website's attractiveness and identify the most effective channels for user acquisition.
Optimization Tip: If your user count is low, consider enhancing your SEO campaigns or online advertisements. Read more: SEO Checklist to Increase Traffic
Sessions
Sessions represent a sequence of interactions a user performs on your website within a specific timeframe. A single user can initiate multiple sessions.
- When does a session start and end?
- Starts: When a user visits your website.
- Ends: After 30 minutes of inactivity or when the user leaves the site and does not return within 30 minutes.
Sessions help measure the level of user interest in your website.
Example: A user visits the homepage, navigates to a product page, and leaves. This entire process counts as one session.
Pageviews
Pageviews indicate the total number of pages viewed by users, including repeated views of the same page. This is a basic metric to evaluate user interaction with your content.
- How to optimize pageviews?
- Use internal links strategically to encourage users to explore more content.
- Enhance content quality to retain users longer.
Learn more: Effective Internal Linking Strategies
Bounce Rate
The bounce rate is the percentage of users who visit a page and leave without performing any other actions (e.g., clicking, filling out forms, or navigating to another page).
- What does a high bounce rate mean?
- The website does not provide content that meets user needs.
- User experience (UX) issues, such as slow page loading or unfriendly design.
Optimization Tips:
- Ensure your page content aligns with user intent.
- Improve page load speed using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights.
Average Session Duration
This metric measures the average time users spend on your website during a session.
- Why it matters:
A high average session duration indicates that your website content is engaging and retains users effectively.
Note: If the average session duration is low, review your content and user experience to identify areas for improvement.
Conversion Rate
The conversion rate measures the percentage of users who complete a desired action on your website, such as:
- Placing an order.
- Submitting a contact form.
- Signing up for a newsletter.
Google Analytics allows you to set and track conversion rates through Goals or Events.
Example: You can monitor the percentage of users who add products to their cart and complete the checkout process to optimize this funnel.
Practical Applications of Google Analytics
Google Analytics is not just an analytics tool but a powerful platform that helps you optimize every aspect of your website and marketing strategy. Here are some practical applications to improve your online business performance:
Real-Time Analytics
Google Analytics provides real-time reports that allow you to monitor activities occurring on your website at the moment. You can:
- Identify the number of users currently visiting your website.
- Check traffic sources (Google Search, Social Media, or Referral).
- Track the content users are viewing or interacting with.
Practical Use Case: Real-time reports are particularly useful during promotions or special events. You can instantly check campaign performance and make adjustments if necessary.
Demographic Analysis
One of the strengths of Google Analytics is its ability to provide detailed data about your audience’s demographics and interests, including:
- Age and Gender: Gain a clearer understanding of your target audience.
- Interests: Identify user groups interested in your field or product.
- Geographic Location: Discover which regions generate the most traffic to optimize local advertising strategies.
Real-World Benefit: Adjust your content, products, and ad campaigns to better suit each customer segment.
Measuring Marketing Campaign Effectiveness
Google Analytics allows you to track the effectiveness of each marketing channel, from paid ads to SEO, Social Media, and Email Marketing. Key metrics you can analyze include:
- Conversion Rates: Identify which channels generate the most leads or revenue.
- Traffic Sources: Analyze which sources contribute the most visitors.
- Campaign Performance: Measure the success of specific ad campaigns.
Example: If a Facebook Ads campaign has a high conversion rate but lacks sustainability, you might consider reallocating the budget to a more reliable channel like Google Ads.
Improving User Experience
Google Analytics helps you analyze user behavior on your website, enabling you to optimize the user experience (UX):
- Behavior Flow: Track how users navigate through your site and identify bottlenecks.
- Site Speed: Detect and fix issues that slow down your site, which significantly impacts bounce rates.
- Site Search: Identify keywords users search for on your site to optimize content and search functionality.
UX Improvement Tip:
Optimize website speed by compressing images, using a CDN, and regularly testing with Google PageSpeed Insights.
Remarketing and Customer Retargeting
Google Analytics enables you to create specific user lists for remarketing campaigns. You can:
- Target users who added items to their cart but didn’t complete a purchase.
- Create ads tailored to users who visited specific product pages.
- Re-engage loyal customers with special offers or discounts.
Benefit: Remarketing increases conversion rates and optimizes advertising costs.
How Google Analytics Works
Understanding how Google Analytics operates is essential to grasp how data is collected, processed, and transformed into actionable insights. This tool functions through four main stages:
Data Collection
The data collection process begins when you integrate the Tracking Code into your website. This code uses JavaScript to gather information from users, including:
- Device Information: Type of device, browser, and operating system.
- User Behavior: Page views, time spent on pages, navigation flow.
- Demographic Data: Geographic location, age, and gender (if enabled).
- Traffic Sources: Where users are coming from (Google Search, Social Media, Direct, Referral).
This raw data is sent to Google servers for storage.
Configuration
At this stage, Google Analytics filters and formats the data based on the configurations you’ve set in your account. Common configurations include:
- Goals: Track specific actions, such as purchases or form submissions.
- Filters: Exclude unnecessary data, like internal company traffic.
- Channel Grouping: Categorize traffic sources like Organic, Paid Search, Social, and Referral.
Processing
Raw data is processed and transformed into metrics and specific reports. During this phase, Google Analytics:
- Combines raw data with your configurations to generate reports on users, sessions, bounce rates, and conversions.
- Applies filters and channel groupings to present data in the most understandable way.
Reporting
Finally, the processed data is displayed in the Google Analytics interface as visual reports. You can:
- View standard reports like Audience, Acquisition, and Behavior.
- Create custom reports tailored to your business needs.
- Combine data with tools like Google Data Studio to generate more visual and in-depth reports.
Benefits of Understanding the Operational Process
Understanding how Google Analytics collects and processes data will help you:
- Optimize Configurations: Set up appropriate goals and filters for more accurate data.
- Comprehend Data Better: Understand how each metric is calculated to make data-driven business strategies.
- Address Issues Promptly: Detect and fix errors like incorrect tracking codes or inaccurate data.
Pro Tip:
Regularly check the Admin section in Google Analytics to ensure that data is being collected properly and reflects your website's performance accurately.
Guide to Sharing and Managing Google Analytics Data
After setting up Google Analytics, the next step is effectively managing and sharing data with team members or business partners. Here's a detailed guide:
How to Share Google Analytics Data
Sharing data is essential to enable stakeholders to analyze and strategize based on reports. Google Analytics provides flexible permissions for you to control access levels.
Steps to Share Data:
-
Access the Admin Section:
- Log in to your Google Analytics account.
- Under the Account, Property, or View columns, select Account Settings to manage user permissions.
-
Add a New User:
- Enter the email address of the person you want to share with.
- Select the appropriate access level:
- Read & Analyze: View data without changing configurations.
- Edit: Manage and modify settings, including goals and filters.
- Manage Users: Add, remove, or edit permissions for other users.
-
Complete:
- Click "Add" to grant access.
Note: Only grant Edit or Manage Users access to those who genuinely need it to avoid errors or data leaks.
Efficiently Managing Google Analytics Data
Managing Google Analytics data involves more than just sharing—it also requires optimizing how you organize and use the data. Below are some steps to help you manage data effectively:
Use Filters:
- Exclude Internal Traffic: Remove traffic from your company's IP address for more accurate data.
- Segment Traffic: Create separate filters for traffic channels like Organic, Paid Search, or Referral.
Set Up Goals:
- Track critical actions such as purchases, form submissions, or email signups.
- Choose the right goal type:
- Destination Goal: Track visits to specific URLs (e.g., thank-you pages).
- Duration Goal: Measure how long users stay on your site.
- Event Goal: Track specific actions like button clicks or video views.
Customize Reports:
- Create Custom Reports: Display only the data you need, such as traffic sources or conversion rates.
- Use Google Data Studio: Connect Google Analytics data for visually appealing and easily shareable reports.
Integrating Google Analytics with Other Tools
Google Analytics doesn’t operate in isolation; you can integrate it with several tools to enhance data analysis and management:
- Google Ads: Monitor ad performance and optimize budget allocation.
- Google Tag Manager: Simplify tracking code management without editing the website code.
- Google Search Console: Analyze keyword rankings and improve SEO performance.
- CRM Systems: Link customer data with website behavior to create effective remarketing strategies.
Example: Integrating Google Analytics with your CRM allows you to track the customer journey from initial visit to purchase, helping optimize conversion rates.
Common Mistakes When Using Google Analytics
While Google Analytics is a powerful tool for website analysis, many users make common mistakes that lead to inaccurate data or inefficient use of its features. Below are common errors and how to fix them:
Incorrectly Implemented Tracking Code
One of the most frequent errors is not properly installing the Tracking Code, resulting in incomplete data collection.
Symptoms:
- Reports show 0 users or data is not updated.
- Some pages lack data or show inconsistent metrics.
Fix:
- Ensure the tracking code is placed in the
<head>tag on all pages. - Use tools like Google Tag Assistant or Chrome DevTools to verify tracking code functionality.
- If using Google Tag Manager, ensure the GA4 Configuration Tag is activated on all pages.
Not Setting Up Goals
Many users overlook or skip setting up Goals, making it impossible to track key actions on the website.
Why This Matters:
Without Goals, you cannot measure whether users complete important actions like signing up, purchasing, or submitting forms.
Fix:
- Navigate to Admin > Goals and create goals based on your needs, such as:
- Destination Goal: Track specific URLs like
/thank-you. - Event Goal: Track actions like button clicks or video views.
- Destination Goal: Track specific URLs like
Pro Tip: Use Google Analytics to set up Conversion Funnels to monitor the customer journey from start to finish.
Ignoring Critical Reports
Google Analytics offers many reports, but ignoring important ones like Audience, Acquisition, and Conversion means missing out on optimization opportunities.
Key Reports to Focus On:
- Audience: Learn about user demographics and interests.
- Acquisition: Identify the channels driving the most traffic.
- Conversion: Evaluate marketing campaign effectiveness and user actions.
Fix:
- Schedule weekly checks for critical reports.
- Customize reports to display data aligned with your business goals.
Misusing Filters
Filters are a powerful tool to exclude irrelevant data, but misusing them can lead to skewed results.
Common Errors:
- Failing to exclude internal traffic inflates data.
- Not segmenting data by channel or region.
Fix:
- Set up filters to exclude internal IP addresses.
- Create specific filters for each traffic source to analyze channel performance.
Not Integrating with Other Tools
Google Analytics becomes even more powerful when integrated with other tools, but many users miss this opportunity.
Recommended Integrations:
- Google Ads: Monitor paid ad performance.
- Google Search Console: Analyze keyword rankings and SEO improvements.
- Google Tag Manager: Simplify tracking code and event management.
Fix:
- Link your Google Ads and Google Search Console accounts to Google Analytics.
- Use Google Tag Manager to streamline tracking and event monitoring.
Conclusion
Google Analytics is a powerful tool that not only helps you monitor and analyze website data but also provides valuable insights to optimize your online business performance. From understanding user behavior and measuring conversion rates to integrating with other marketing tools, Google Analytics gives you a comprehensive view to improve your website.
Google Analytics is not just a tool; it’s a long-term strategy to enhance user experience, increase traffic, and optimize revenue. Start setting up and leveraging this tool today to take your website to the next level!
Latest Posts

Lesson 26. How to Use break, continue, and return in Java | Learn Java Basics
A guide on how to use break, continue, and return statements in Java to control loops and program execution flow effectively.

Lesson 25. The do-while Loop in Java | Learn Basic Java
A detailed guide on the do-while loop in Java, including syntax, usage, examples, and comparison with the while loop.

Lesson 24. How to Convert Decimal to Binary in Java | Learn Basic Java
A guide on how to convert numbers from the decimal system to the binary system in Java using different methods, with illustrative examples.

Lesson 23. How to Use the While Loop in Java | Learn Java Basics
Learn how to use the while loop in Java with syntax, real-world examples, and practical applications in Java programming.
Related Posts

What is CRM Software? Top 15+ Best Customer Relationship Management Software
Discover the definition of CRM software, its role in customer relationship management, and a list of 15+ top CRM solutions to help businesses enhance customer service performance and achieve sustainable growth.

What Is Local Guide? Benefits of Becoming a Local Guide on Google Maps
Local Guide is a community program by Google Maps where users can contribute reviews, photos, and location information to improve map data. This article explains what Local Guide is and the benefits of being an active member.

What is Zalo OA? A Detailed Guide to Creating Zalo Official Account for Businesses
Zalo Official Account (Zalo OA) is a crucial tool that helps businesses connect with customers and optimize their online business operations. This article provides a step-by-step guide on how to create a Zalo OA from A to Z.
What is Zalo Ads? A Guide to Running Effective Zalo Ads
Discover what Zalo Ads are and learn how to run effective Zalo advertising campaigns to reach customers and boost sales in the digital era.

