Understanding Hosting – Types of Web Hosting, Pros and Cons, and How to Choose the Right Option
- Published on

- What is Hosting?
- Why is Hosting Important?
- Key Benefits of Hosting:
- Different Types of Web Hosting
- Shared Hosting
- VPS Hosting
- Cloud Hosting
- Dedicated Server Hosting
- WordPress Hosting
- Comparison Table
- How Does Web Hosting Work?
- Role of Hosting Providers
- Role of Users
- How Web Hosting Works
- The Role of Web Hosting in Businesses
- Ensuring Continuous Online Presence
- Impact on Website Speed and Performance
- Securing Your Data
- Flexible Scalability
- Enhancing Brand and Credibility
- Key Web Hosting Metrics You Should Know
- Storage
- Bandwidth
- CPU and RAM Resources
- Uptime
- SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) Support
- Database Support
- Backup Features
- Technical Support Features
- What Is the Difference Between Domain and Web Hosting?
- Domain
- Web Hosting
- Key Differences
- The Relationship Between Domain and Web Hosting
- Free Hosting vs. Paid Hosting
- Free Hosting
- Paid Hosting
- When to Use Free Hosting and Paid Hosting?
- Platforms to Create Websites Without Hosting
- Wix
- Weebly
- WordPress.com
- Shopify
- Squarespace
- Advantages of These Platforms
- Disadvantages
- Guide to Choosing Good Hosting
- Choose the Right Hosting Type
- Hosting Plan Pricing
- Customer Support Policies
- Where to Buy Good Hosting
- Conclusion
What is Hosting?
Hosting, also known as web hosting, is an online storage service where you can store all the necessary data and files for a website to function. When a user enters your website's address (domain name) into a browser, the hosting system delivers files and information from the server to the browser, allowing users to easily access your website.

Simply put, hosting is the “home” of a website on the internet, storing all content such as images, videos, articles, and other data files. To run a website, you need both a domain name and hosting. If the domain is the address, hosting is the foundation on which your website is built.
Why is Hosting Important?
A high-quality hosting service not only ensures your website is always online and accessible but also directly impacts loading speed, user experience, and SEO rankings on search engines. Without hosting, your website cannot be accessed via the internet.
Key Benefits of Hosting:
- High Availability (Uptime): Ensures your website is always operational, minimizing downtime.
- Security: Quality hosting includes features like SSL, DDoS protection, and regular backups.
- Performance: Provides sufficient resources to ensure fast loading speeds, benefiting both users and search engines.
Different Types of Web Hosting
Web hosting is divided into several types based on how resources are allocated and managed. Below are the common types of hosting suitable for various website needs and levels of development:
Shared Hosting
Shared Hosting is a type of hosting where multiple websites share resources on the same physical server. These include CPU, RAM, storage, and bandwidth. Shared hosting is often an ideal choice for individuals or small businesses starting their websites due to its low cost and ease of use.

Advantages of Shared Hosting:
- Low cost: The cheapest hosting option, suitable for beginners.
- Easy management: Often includes control panels like cPanel or Plesk for simple website setup and management.
- No technical expertise required: Users don't need to worry about server management.
Disadvantages of Shared Hosting:
- Unstable performance: Shared resources mean your website’s performance may be affected by traffic spikes on other websites on the same server.
- Limited control: Users do not have root access or deep customization options.
- Lower security: If another website on the same server is attacked, your website's security risk increases.
Shared Hosting is best suited for personal websites, blogs, or small business sites with low traffic.
VPS Hosting
VPS Hosting (Virtual Private Server) provides users with a private virtual server on the same physical server. Although resources are shared with other users, each VPS has its own allocated resources (RAM, CPU, storage) to ensure stable performance.
Advantages of VPS Hosting:
- Better performance: Not affected by the traffic of other websites.
- Higher control: Users have root access, allowing for server customization as needed.
- Improved security: Each VPS operates as an independent environment.
Disadvantages of VPS Hosting:
- Higher cost: More expensive than shared hosting.
- Requires technical knowledge: Users need server management skills for configuration and maintenance.
VPS Hosting is suitable for medium-sized businesses or websites with moderate traffic requiring higher performance.
Cloud Hosting
Cloud Hosting uses a network of cloud servers to host websites. Instead of relying on a single server, website data is distributed across multiple servers, increasing flexibility and scalability.

Advantages of Cloud Hosting:
- Flexible scalability: Resources can be increased or decreased quickly as needed.
- Stable performance: If one server fails, the system automatically switches to another.
- Suitable for high traffic: Ideal for websites or applications with a large user base.
Disadvantages of Cloud Hosting:
- Variable costs: Prices can fluctuate based on resource usage.
- More complex: Cloud hosting requires more technical management.
Cloud Hosting is an ideal choice for large enterprises, e-commerce websites, or applications requiring high performance and stability.
Dedicated Server Hosting
Dedicated Hosting is the most premium type of hosting, where an entire physical server is dedicated to one customer. Without sharing resources, this hosting type provides maximum control and the highest performance.
Advantages of Dedicated Hosting:
- Highest performance: All server resources are exclusively for one website.
- Full control: Users can customize all server configurations.
- Superior security: No resource sharing means reduced security risks.
Disadvantages of Dedicated Hosting:
- High cost: The most expensive hosting option.
- Requires advanced technical skills: Users need in-depth knowledge to manage the server.
Dedicated Hosting is suitable for large businesses or websites with very high traffic requiring maximum security and performance.
WordPress Hosting
WordPress Hosting is a hosting service designed specifically for websites using the WordPress platform. This type of hosting is usually optimized for performance, security, and built-in tools tailored to WordPress.
Advantages of WordPress Hosting:
- Optimized performance: Configured specifically to boost loading speeds for WordPress websites.
- Ease of use: Includes features like 1-click installation and automatic updates.
- Specialized support: Technical support focuses on WordPress-related issues.
Disadvantages of WordPress Hosting:
- Platform limitation: Only suitable for WordPress-based websites.
- Potentially higher cost: Can be more expensive than Shared Hosting.
WordPress Hosting is the best choice for those wanting to build a professional WordPress website without requiring extensive technical knowledge.
Comparison Table
| Hosting Type | Advantages | Disadvantages | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shared Hosting |
|
| Personal websites, blogs, small businesses |
| VPS Hosting |
|
| Medium-sized businesses, websites with moderate traffic |
| Cloud Hosting |
|
| Large enterprises, e-commerce websites |
| Dedicated Server Hosting |
|
| Large businesses, websites with very high traffic |
| WordPress Hosting |
|
| WordPress websites, professional bloggers |
How Does Web Hosting Work?
To understand how Web Hosting works, you need to know about its two main components: hosting providers and users. Each plays a critical role in ensuring your website operates smoothly and is accessible from anywhere on the internet.
Role of Hosting Providers
Hosting providers are responsible for offering the infrastructure and technology required to host a website. Here are the main responsibilities they handle:
- Server Management: Includes maintaining hardware, operating systems, and server software to ensure the server remains operational.
- Resource Allocation: Divides resources (CPU, RAM, bandwidth, storage) based on the hosting plan you choose.
- Security: Offers security features like SSL, DDoS protection, and malware defense.
- Technical Support: Helps customers with hosting-related issues, from setup to troubleshooting.
Role of Users
Users, or website owners, are responsible for managing and running their content on the hosting space provided. User responsibilities include:
- Uploading Files to Hosting: All files such as HTML, CSS, JavaScript, images, and videos must be uploaded to the server.
- Installing Content Management Systems (CMS): Platforms like WordPress, Joomla, or Drupal make it easy to build and manage websites.
- Database Management: Dynamic websites require databases (e.g., MySQL, PostgreSQL) to store information.
- Configuring DNS (Domain Name System): Users must connect their domain to hosting via DNS to make the website accessible through its domain name.
How Web Hosting Works
- When a user enters a domain name (e.g., www.example.com) in a browser, the browser sends a request to a DNS server to locate the IP address of the hosting server.
- The DNS server returns the IP address where the website is hosted.
- The browser connects to the hosting server via the IP address and downloads the website files.
- The website is displayed on the user's browser.
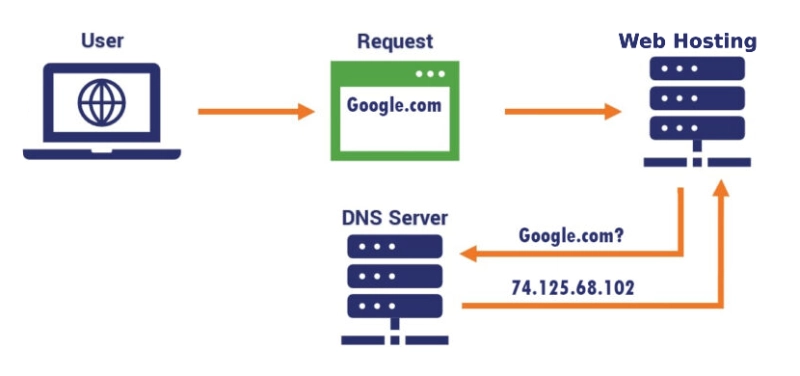
Web hosting acts as a bridge, ensuring your content is always available to users. It is an essential factor in maintaining your online presence.
The Role of Web Hosting in Businesses
Web hosting plays a vital role in maintaining a business's online presence, directly influencing how customers access, interact with, and perceive your brand. A good hosting solution not only ensures stable website operations but also offers strategic value to businesses.
Ensuring Continuous Online Presence
- Hosting keeps your website online, ready to serve customers 24/7.
- High uptime is crucial for retaining customers and maintaining revenue, especially for e-commerce businesses.
Impact on Website Speed and Performance
- High-quality hosting ensures faster website loading times, improving user experience (UX) and reducing bounce rates.
- Better performance also helps improve SEO rankings, driving more traffic to your site.
Securing Your Data
- Reliable hosting providers often include security features such as SSL certificates, regular backups, and DDoS protection.
- For businesses handling sensitive information like customer data, these features build trust and ensure compliance with legal data protection regulations.

Flexible Scalability
- As businesses grow, hosting needs increase. Hosting solutions like VPS or Cloud Hosting make it easy to scale resources without migrating the entire website.
- This is particularly important for businesses planning to expand or expecting increased traffic in the future.
Enhancing Brand and Credibility
- A stable, fast, and secure website leaves a positive impression on customers, strengthening your brand image.
- For businesses, web hosting is an integral part of building a professional online presence.
Web hosting is more than just a technical foundation; it’s a strategic component for achieving online business goals. Choosing the right hosting type for your needs not only saves costs but also significantly improves user experience and website performance.
Key Web Hosting Metrics You Should Know
When purchasing a hosting service, understanding the technical metrics is crucial to ensure the hosting meets your website's needs. Below are the key factors to consider:
Storage
- This is the storage space provided by the hosting provider to hold all your website files, including images, videos, databases, and source code.
- Recommended:
- Small, personal websites: 1GB - 5GB.
- Business or e-commerce websites: Larger storage, typically 10GB or more.
Bandwidth
- Bandwidth refers to the amount of data transferred between your website and users within a specified period (usually monthly).
- Notes:
- Websites with many videos, images, or high traffic require more bandwidth.
- Many providers now offer unlimited bandwidth, but check usage policies for hidden limits.
CPU and RAM Resources
- CPU: Determines how fast your server can process user requests, affecting load times.
- RAM: Higher RAM allows better handling of concurrent tasks.
- Recommendation: Small websites can work with 1 CPU and 512MB - 1GB RAM, while larger websites or complex applications may require 2GB RAM or more.
Uptime
- Uptime measures the percentage of time a server is operational without issues. It’s typically expressed as a percentage.
- Good Standard: 99.9% uptime to ensure the website is always online.
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) Support
- SSL encrypts data between the browser and server, protecting user information and increasing website trust.
- Today, SSL is not only a security requirement but also crucial for improving SEO.
Database Support
- Most hosting services support popular database management systems like MySQL, PostgreSQL, or MSSQL.
- Ensure the hosting service meets your database requirements in terms of type and quantity.
Backup Features
- Good hosting services include automated data backups, ensuring you can restore data if something goes wrong.
- Consider backup frequency (daily, weekly) and quick recovery options.
Technical Support Features
- Verify if the provider offers 24/7 support through multiple channels (chat, email, phone).
- Quick and professional technical support is vital for resolving issues promptly.
What Is the Difference Between Domain and Web Hosting?
When building a website, you'll often encounter the terms domain and web hosting, but many people confuse the two. Below is a clear distinction:
Domain
- Definition: A domain is a unique address that helps users find your website on the internet, e.g.,
www.example.com. - Role: A domain acts as the "address" of your house. It makes it easy for users to access your website instead of remembering a complex IP address.
- Components:
- Top-Level Domain (TLD): Examples include
.com,.net,.org. - Second-Level Domain: Your unique name, e.g.,
exampleinexample.com.
- Top-Level Domain (TLD): Examples include
Web Hosting
- Definition: Web hosting is the space on a server where all your website files and data are stored.
- Role: Hosting is like the "land" on which your website is built. The website data is stored on the server and accessed via the domain name.
Key Differences
| Factor | Domain | Web Hosting |
|---|---|---|
| Role | The address to access the website | The place to store website data |
| Primary Function | Helps users easily find the website | Stores and delivers website content |
| Requirement | Does not work without being connected to hosting | Cannot be accessed without a domain |
The Relationship Between Domain and Web Hosting
- To make a website operational, you need both a domain and hosting. When users enter a domain name into their browser, the DNS system directs them to the hosting server where the website is stored.
- Example: When entering
www.example.com, the browser queries the DNS to find the hosting server containing the website’s data and displays the content.
Free Hosting vs. Paid Hosting
When choosing hosting for a website, you’ll encounter two main options: Free Hosting and Paid Hosting. Each has its own pros and cons, suitable for different use cases.
Free Hosting
Free Hosting is a service that provides storage space for websites at no cost. It’s often offered by website builders or hosting companies for advertising purposes.
Advantages:
- No Cost: Ideal for beginners or those wanting to experiment with building a website without investment.
- Easy to Sign Up: No complicated procedures; you can start using it immediately after registration.
Disadvantages:
- Limited Resources: Storage and bandwidth are usually very restricted.
- Mandatory Ads: The provider may place ads on your website, making it less professional.
- Poor Performance: Slow loading speeds and frequent interruptions during high traffic periods.
- Limited Technical Support: Assistance may be unavailable or minimal when issues arise.
Best For:
- Beginners learning how to build a website.
- Small projects or experimental use cases.
Paid Hosting
Paid Hosting is a service requiring periodic payments (monthly or yearly) for usage. It’s the go-to option for professional websites.
Advantages:
- Stable Performance: Provides ample resources, fast speeds, and high uptime.
- Better Security: Includes advanced security features like SSL, automated backups, and DDoS protection.
- 24/7 Technical Support: Dedicated support teams are available to resolve issues promptly.
- No Ads: Ensures a more professional look without intrusive ads from providers.
Disadvantages:
- Higher Cost: May not fit the budget of small businesses or individuals.
- Long-Term Commitment: Some plans require upfront payment for extended periods.
Best For:
- E-commerce websites, businesses, or individuals looking to build a professional brand.
- Projects requiring speed, security, and scalability.
When to Use Free Hosting and Paid Hosting?
The decision between Free Hosting and Paid Hosting depends on your purpose and actual needs. Below are scenarios to consider:
When to Choose Free Hosting?
- Learning and Practice:
- Free hosting is suitable for those just starting to learn how to create and manage websites. You can practice building basic sites without worrying about costs.
- Experimental Projects:
- If you only need a website to test ideas or features, free hosting is a budget-friendly option.
- Simple Personal Websites:
- Personal blogs, small portfolios, or basic websites that don’t require significant storage or advanced features can run well on free hosting.
When to Choose Paid Hosting?
- Building Professional Websites:
- If you’re building a website for a business or personal brand, paid hosting is essential to ensure fast load times, security, and stability.
- E-commerce Websites:
- Online stores need to handle sensitive customer data and financial transactions, requiring the high performance and security that only paid hosting can provide.
- High-Traffic Websites:
- Free hosting cannot meet the demands of high-traffic websites. If you anticipate many users visiting your site, opt for paid hosting to avoid service disruptions.
- Advanced Customization Needs:
- Large projects requiring specific technologies or server customizations need VPS, Cloud Hosting, or Dedicated Server – all of which are paid services.
Quick Comparison
| Criteria | Free Hosting | Paid Hosting |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Free | Periodic payment required |
| Performance | Low | High |
| Storage | Limited | Depends on the plan |
| Security | Low, not guaranteed | High, with many security features |
| Technical Support | None or very limited | Professional, 24/7 |
| Best Suited For | Learning, experimenting, small projects | Businesses, professional websites |
- Free Hosting is a suitable option if you have no budget or only need a temporary solution for simple projects, learning, or experimentation.
- Paid Hosting is a necessary investment if you want to develop a professional, reliable, and scalable website for future growth.
Choosing the right hosting type will directly affect the performance of your website, so consider your goals and specific needs carefully.
Platforms to Create Websites Without Hosting
You don't always need a separate hosting service to build a website. Today, many platforms provide solutions to create websites without requiring users to purchase or manage hosting. Here are some popular platforms:
Wix
- Features: Wix is an intuitive drag-and-drop website builder. It offers free hosting and domain (with ads) or paid plans (ad-free with more features).
- Best For: Individuals and small businesses who want to quickly create a website without technical skills.
Weebly
- Features: Similar to Wix, Weebly provides tools to design websites without needing separate hosting. Both free and paid plans are available.
- Best For: Personal blogs or small business websites.
WordPress.com
- Features: WordPress.com (different from WordPress.org) is a platform that allows you to create and host websites for free or through paid plans for additional features. Users don’t have to worry about hosting as it’s managed entirely by WordPress.
- Best For: Personal blogs or basic websites.
Shopify
- Features: Shopify is an e-commerce platform that offers everything from website design to hosting and payment integration. No separate hosting is needed as Shopify provides an all-in-one solution.
- Best For: Online stores and e-commerce businesses.
Squarespace
- Features: Squarespace is a premium website builder with beautiful templates optimized for non-technical users. Hosting is integrated into the service.
- Best For: Medium-sized businesses, portfolios, or creative websites.
Advantages of These Platforms
- Easy to Use: No technical skills required.
- All-in-One: Hosting, design, and website management tools are integrated.
- Quick Setup: You can have a basic website running in just a few hours.
Disadvantages
- Limited Customization: You are restricted to the tools and templates provided by the platform.
- Potentially Higher Costs: Paid plans can be more expensive than buying hosting and designing yourself.
- Platform Dependency: Migrating your website to another platform can be challenging.
These platforms are excellent for those who want to quickly build a website without much technical knowledge or hosting management. However, if you need a deeply customizable website with full control, using separate hosting is a better choice.
Guide to Choosing Good Hosting
Selecting the right hosting is crucial to ensure your website operates stably, securely, and meets future growth needs. Below are factors to consider when choosing a hosting service.
Choose the Right Hosting Type
-
Shared Hosting:
- Suitable for personal websites, blogs, or small businesses with low traffic.
- This is a cost-effective choice but limited in performance and security.
-
VPS Hosting:
- Ideal for medium-sized businesses or websites requiring better performance.
- VPS offers more customization and dedicated resources.
-
Cloud Hosting:
- Perfect for e-commerce websites or those with high traffic.
- This service offers flexible scalability and ensures high performance.
-
Dedicated Hosting:
- Suitable for large websites or applications needing powerful resources and high security.
- This is an expensive option but offers maximum performance and control.
-
WordPress Hosting:
- Optimized for websites built on WordPress, with easy installation and robust security.
Hosting Plan Pricing
- Determine Your Budget: Decide how much you can invest monthly or annually.
- Long-Term Savings: Many providers offer discounts for long-term subscriptions (1-3 years).
- Check Pricing Policies: Be aware of hidden costs, renewal fees, or additional services (SSL, backups).
Customer Support Policies
- Technical Support: Prioritize providers offering 24/7 support through multiple channels like email, live chat, or phone.
- Response Time: Read customer reviews to determine if the support team is responsive and professional.
- Self-Help Resources: Check for articles, guides, or video tutorials provided by the hosting company.
Where to Buy Good Hosting
- Reputable Providers: Choose from well-known providers like Bluehost, Hostinger, SiteGround, HostGator, or A2 Hosting.
- User Reviews: Read real user reviews on platforms like Trustpilot, G2, or Reddit.
- Money-Back Guarantee: Prefer providers with refund policies if you are dissatisfied with the service.
Detailed purchase guide: How to Buy Hosting for Your Website
Conclusion
Understanding hosting and choosing the right service is a key step in building and operating a website. Hosting is not just where your data is stored but also a critical factor in determining performance, security, and user experience.
Whether you choose free hosting or paid hosting, the core requirement is that it meets the current needs of your website and can scale as the website grows. Carefully consider factors like hosting type, pricing, support policies, and security capabilities before making a decision. Especially, choosing a reputable provider ensures stability and data protection for your website.
A good hosting service not only brings peace of mind but also lays the foundation for developing your brand and establishing credibility online. Invest wisely to ensure your website operates effectively and optimally!
Latest Posts

Lesson 26. How to Use break, continue, and return in Java | Learn Java Basics
A guide on how to use break, continue, and return statements in Java to control loops and program execution flow effectively.

Lesson 25. The do-while Loop in Java | Learn Basic Java
A detailed guide on the do-while loop in Java, including syntax, usage, examples, and comparison with the while loop.

Lesson 24. How to Convert Decimal to Binary in Java | Learn Basic Java
A guide on how to convert numbers from the decimal system to the binary system in Java using different methods, with illustrative examples.

Lesson 23. How to Use the While Loop in Java | Learn Java Basics
Learn how to use the while loop in Java with syntax, real-world examples, and practical applications in Java programming.
Related Posts

What is .htaccess? Guide to Editing and Configuring .htaccess
Learn about the .htaccess file, its functions, and how to edit and configure .htaccess to optimize security, SEO, and website performance.

What is DNS? The Mechanism of Domain Name Resolution System
Learn about DNS, the mechanism of the domain name resolution system, and the important role of DNS in maintaining website operations.

What is a Dedicated Server? A Guide to Choosing the Right Dedicated Server
Learn about Dedicated Servers, the benefits of using a dedicated server, and how to choose the right one for your needs.
Difference Between Web Server and Application Server
Learn the difference between Web Server and Application Server – two essential servers in web technology systems. Explore their structure, functions, how they work, and when to use each type of server.

